Foot care for diabetics is crucial for overall health management. Introduction to Diabetic Foot Care emphasizes the importance of this care in preventing serious complications. While diabetes can often be managed with medication and lifestyle changes, it presents unique challenges, particularly concerning foot health. One major issue is peripheral neuropathy, which affects sensation in the feet, reducing the ability to detect injuries and infections.
Unfortunately, many diabetics may not fully understand the effects of neuropathy on their foot health. This lack of awareness can lead to severe consequences like ulcers and infections, potentially escalating into more dire situations. Thus, educating patients on effective foot care is essential for maintaining healthy feet and overall well-being.
Contents
Introduction to Foot Care for Diabetic Patients: Understanding Nerve Damage (Neuropathy)

Diabetic neuropathy refers to nerve damage caused by prolonged high blood sugar levels. Its effects extend beyond discomfort, fundamentally altering how individuals perceive sensations in their feet, significantly impacting daily life.
Understanding Neuropathy
Neuropathy in diabetic patients arises when elevated glucose levels cause damage to the peripheral nerves. These nerves are responsible for sending messages between the brain and the rest of the body, including the feet. As nerve function deteriorates, patients may experience symptoms ranging from tingling sensations to complete loss of feeling.
This condition can lead to a dangerous cycle where minor injuries go unnoticed. For instance, an unnoticed blister may develop into a serious wound, leading to infections that could jeopardize the individual’s mobility or even necessitate amputation. Thus, understanding the multifaceted nature of neuropathy is crucial for anyone managing diabetes.
Symptoms and Effects
Common symptoms of diabetic neuropathy include numbness, tingling, and sharp pain in the feet. The discomfort can vary greatly among individuals, and some may not experience any sensations at all.
The progressive nature of neuropathy means that initial symptoms could either worsen over time or, in some cases, plateau after reaching a certain threshold. Regardless of the path it takes, the underlying problem remains: diminished sensation leads to inadequate protection for the feet.
As neuropathy advances, the risk of developing foot deformities increases as well. These deformities may arise from uneven weight distribution caused by discomfort, leading to further complications such as bunions or hammertoes. Therefore, recognizing the signs of nerve damage early on can facilitate timely interventions and potentially avoid severe consequences.
Preventive Measures

Prevention strategies for neuropathy-related foot issues should begin with regular monitoring of blood glucose levels. By maintaining better control over blood sugar, individuals can reduce the likelihood of nerve damage. Regular check-ups with healthcare practitioners specifically focused on foot health are equally vital.
Daily self-examinations of the feet can help identify any potential issues such as cuts, blisters, or areas of redness. Empowering individuals with knowledge about how to conduct these examinations will enable them to take ownership of their foot care routines, which is a critical component in safeguarding against diabetic complications.
Additionally, wearing appropriate footwear is paramount. Shoes should offer sufficient support and cushion while being the right size to prevent friction or pressure points. This simple yet effective step can provide a layer of protection against injuries that may go unnoticed due to neuropathy.
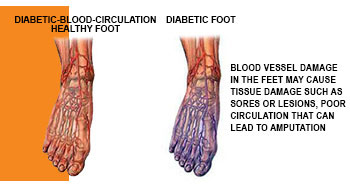
Poor blood circulation in the feet

Another significant challenge faced by diabetic individuals is poor blood circulation, particularly in the feet. Diabetes can negatively affect blood vessels and circulation, compounding the difficulties already posed by neuropathy.
The Role of Circulation
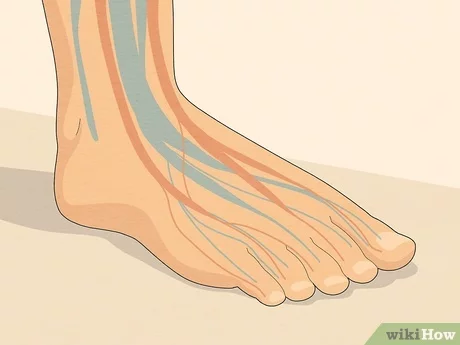
Blood circulation is essential for delivering oxygen and nutrients to various parts of the body, including the feet. People with diabetes often experience conditions such as peripheral artery disease, which reduces blood flow to these extremities. As a result, tissues may become deprived of necessary sustenance, impairing their ability to heal and regenerate.
Poor circulation creates a scenario where even minor injuries can escalate quickly. For example, if a person cuts their foot, the healing process might be hindered due to insufficient blood supply. Without timely intervention, such injuries can worsen, leading to infections and ulcers that become increasingly difficult to manage.
Impact of Lifestyle Choices
Lifestyle choices significantly influence blood circulation. Factors such as smoking, obesity, and inactivity can exacerbate circulatory problems among those diagnosed with diabetes. When these elements combine with the effects of high blood glucose levels, the outcome can be troubling.
Encouraging patients to adopt healthier habits can alleviate some of the circulatory challenges they face. Engaging in regular exercise can improve overall cardiovascular health and promote better blood flow. Simple activities such as walking or swimming can make a considerable difference over time.
Moreover, maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can play a crucial role in enhancing circulation. Nutrients found in these foods contribute to vascular health, helping to ensure that blood reaches the lower extremities effectively. This connection between dietary choices and circulation emphasizes the importance of holistic care approaches that encompass both nutrition and physical activity.
Recognizing Common Symptoms
Individuals suffering from poor blood circulation may notice changes such as cold feet, pale skin, or slow-healing wounds. It is imperative for patients to remain vigilant for these warning signs and seek medical attention when necessary.
Regularly scheduled appointments with healthcare professionals can help monitor blood circulation and assess any emerging concerns. Additionally, performing self-checks at home can empower patients to stay informed about their own health status. Emphasizing personal responsibility in monitoring one’s health can foster a proactive attitude toward care.
By addressing both neuropathy and poor blood circulation together, diabetic individuals can significantly improve their chances of avoiding serious foot complications.
And how these problems can lead to ulcers and infections if not taken care of promptly time.
Poor circulation and neuropathy can lead to serious issues, increasing the risk of ulcers and infections in diabetics, which severely affect their quality of life.
Understanding Foot Ulcers
Foot ulcers often arise from prolonged pressure on specific areas. Diabetic patients may not feel injuries due to neuropathy, allowing seemingly minor wounds to escalate if untreated.
Contributing factors include ill-fitting shoes, foot deformities, and existing injuries. Preventing foot ulcers requires a comprehensive approach emphasizing regular foot care and monitoring.
Risk of Infection
Ulcers signal larger issues, often leading to infections due to poor healing abilities linked to bad circulation. Bacteria can easily enter open wounds, potentially causing severe systemic infections requiring hospitalization.
Patients may experience slow healing, resulting in chronic infections and increased risks of severe complications like amputations. Awareness of these risks is crucial for understanding potential undermining problems associated with untreated foot conditions.
Importance of Prompt Attention
Timely medical intervention is vital to manage ulcers and infections effectively. Diabetics should consult healthcare providers at the first sign of injury; early treatment improves outcomes.
Educating patients on proper home care techniques enhances their defense against complications, including careful wound hygiene and monitoring for changes in color or odor.
Regular foot checks are essential to detect potential issues early. Open communication between patients and healthcare teams fosters a supportive environment for effective foot care.
Conclusion
Proper diabetic foot care is crucial for managing diabetes. By addressing related issues, individuals can reduce complications. Increased awareness of neuropathy and circulation challenges empowers patients to take control of their foot health. Through education, lifestyle adjustments, and regular check-ups, risks associated with foot ulcers and infections can be minimized, ultimately maintaining mobility and independence. A multi-faceted approach will promote healthier living while navigating diabetes complexities.
.





